Singing in Ancient Egypt
Although the ancient Egyptian always appeared to be preoccupied with his afterlife, singing played a prominent role in his earthly life as well as in the afterlife. Music and singing for the ancient Egyptians were food for the soul. They used them during harvest, in the fields, at the birth of a new child, at weddings, and even in funeral processions. Music was an important feature in the life of the ancient Egyptians. One of the most remarkable things that indicates the intelligence of the ancient Egyptians is that they had musical bands. Some of these bands consisted of the blind because the blind are always stronger in hearing than others. Musical bands in ancient Egypt were not only composed of singers but also included female singers and musicians who played musical instruments. And this form is still used in all musical bands around the world. The ancient Egyptians also used musical bands in their social gatherings, especially those he held in his home for their guests or their private parties with their wife and children, such as birthdays. Birthdays were not only for the elite, but we found in the tombs of the workers who built the Great Pyramid that one of them was absent to prepare for his daughter’s birthday. Even some musicians were stars of society in their time. -A blind harpist from the tomb of Nekht in the Theban Necropolis.
A musical band clapping their hands
A musical band clapping their hands (Middle Kingdom, reign of Mentuhotep II, Deir el-Bahri – Cincinnati Art Museum – Ohio – United States)]
A band of two sisters
A band of two sisters, Hekenu playing the harp and her sister Ati singing.
Egyptian girls form an ancient musical band of beautiful girls from 3400 years ago
In upper image, Egyptian girls form an ancient musical band of beautiful girls from 3400 years ago, and in the lower image Egyptian girls dating to 1934. (Genes are inherited through generations.)
Dance in Ancient Egypt
Dance for the ancient Egyptian was initially a type of religious ritual, not merely a spectacle of entertainment as it is now. In fact, some temples in Memphis had dance schools. Dance was used to celebrate the construction of new temples. It was also used in coronation ceremonies. As for worldly matters, dance was for the elite in their parties, and dance and singing were considered a sign of the wealth of the party host. If the party included Egyptian dancers, this indicated the importance of the host and the guests. If the party included foreign dancers, this was considered a lesser social status for the ancient Egyptians. The ancient Egyptians did not only use dancers in social occasions such as weddings but also used them in their own celebrations with their wives and children. The ancient Egyptians were fond of cleanliness. Therefore, before dancing, the dancers used a type of funnel-shaped perfume to perfume not only their bodies but also their hair. Thus, when they moved, the perfume filled the place, and the spectators felt visual comfort from seeing the dancers and respiratory comfort from smelling the finest perfumes. The dancers used belts around their waists. One of the most striking things about the dancers is that they used to draw tattoos on their legs in the form of the god of laughter, joy, and happiness, the god Bes.
Types of Dances
Individual or Pair Dances: These were dedicated to harvest celebrations, performed by the king or his deputy to celebrate the beginning of the harvest, offering sacrifices along with dancing to the gods Min, the god of fertility, and Renenutet, the goddess of grain and harvest. They were also known for using sticks in their dances.
Group Dances
Group dances were used either in grand celebrations in front of the king and his guests or in funerary rituals. The girls who performed group dances were always trained in special dance schools. A dance trainer would teach them movement with rhythm, whether by clapping or drumming, and they would move like ballerinas today in organized and group movements.
Use of Dwarfs in Dance
Use of Dwarfs in Dance: Dwarfs, by their nature, were more flexible in movement due to their small size. Therefore, they performed acrobatic dances in celebrations, especially when there were children enjoying the party, or if the king or prince was a child, he would enjoy the dwarf’s dances and acrobatic movements. The ancient Egyptians not only used dwarfs and dancers but also monkeys. They trained them and used them in their celebrations, especially in large celebrations such as the Opet festival for the god Amun-Ra, which was the largest festival of the Egyptian empire. Dance was also used in funerary rituals, as seen in the tombs of West Thebes.
A scene of dancers and musicians from the tomb of Nebamun in Luxor.
A scene depicting a dancer performing acrobatic movements, displayed in the Egyptian Museum in Turin
A SCENE OF MUSICIANS FROM THE TOMB OF NEKHT IN LUXOR
The Most Important Musical Instruments
The most important musical instruments that we know about from the ancient Egyptians are: Stringed instruments such as the harp (cello today), the ginj (guitar today), and the oud. Wind instruments, which are the oldest instruments known to the ancient Egyptians, such as the nay (flute). The ancient Egyptians also used instruments like the sistrum (shaker) and instruments like the drum and the tambourine. This indicates how rich Egypt was with its generosity, arts, and favors that taught the world arts, literature, and music at a time when the world was drowning in ignorance and backwardness.
A musician playing a stringed instrument from ancient Egypt.
Oud and flute players in the tomb of Nebamun in Luxor.
The sistrum or shaker, dedicated to the goddess Hathor.
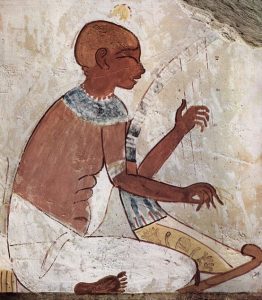
The harp Player
THE guitar is ancient Egyptian instrument
THE guitar is ancient Egyptian instrument, which has continued since the time of the pyramid builders and until the nowadays guests of the pyramids (Shakira with a guitar in front of the pyramids in 2007).
Generations after generations
A tambourine player from ancient Egypt versus a tambourine player from the ceremony of royal mummies transfer. Generations after generations live on artistic creativity from ancestors to descendants.